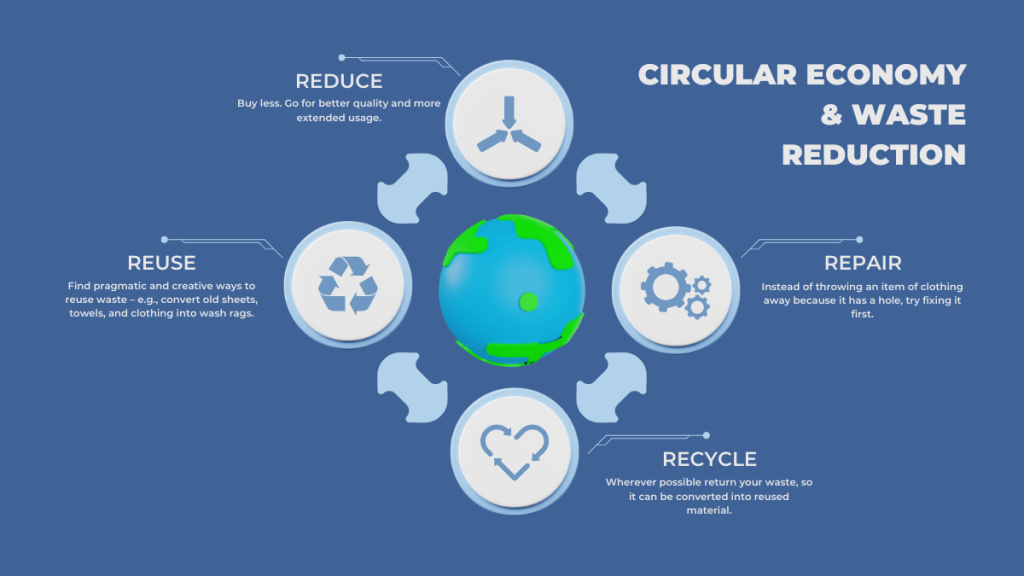
In a world increasingly aware of the environmental consequences of unchecked consumerism and wasteful production practices, the concept of a circular economy has emerged as a beacon of hope.
Unlike the traditional linear economy that follows a “take, make, dispose” pattern, the circular economy envisions a more sustainable approach to resource management, where materials are continually recycled, repurposed, and reused. This article explores the core principles of the circular economy, its undeniable benefits in waste reduction, and its role in shaping a greener, more equitable future.
The Core Principles of a Circular Economy
1. Design for Durability and Recyclability
At the heart of the circular economy lies the principle of designing products for longevity and recyclability. Manufacturers are encouraged to craft goods with materials that can be easily dismantled and repurposed at the end of their life cycle. This approach not only reduces the amount of waste destined for landfills but also conserves valuable resources by allowing them to be extracted and reused in new products.
2. Embrace Sharing and Collaborative Consumption
Imagine a world where the mantra “own less, share more” guides our consumption habits. This is the essence of the sharing economy, a concept that dovetails seamlessly with the circular economy. Sharing platforms and collaborative consumption models, like ridesharing services and tool libraries, encourage people to access goods as needed, rather than owning them outright. This not only minimizes overproduction but also cultivates a sense of community and reduces the demand for raw materials.
3. Implement Reverse Logistics
The circular economy thrives on the idea that products should have multiple lives. Reverse logistics, the process of bringing used items back into the production cycle, is a critical aspect of achieving this. Through refurbishment, remanufacturing, and recycling, products can be given a second chance at usefulness. This not only diverts waste from landfills but also curbs the need for new resource extraction.
The Benefits of a Circular Economy
1. Reduction in Resource Depletion
In a world where the extraction of finite resources has reached unsustainable levels, the circular economy offers a lifeline. By emphasizing the reuse and recycling of materials, the circular model reduces the strain on our planet’s resources. This, in turn, helps safeguard delicate ecosystems, reduce energy consumption, and curb the environmental toll of resource extraction.
2. Decreased Waste Generation
One of the most glaring issues of our linear economy is the staggering amount of waste it generates. From single-use plastics to discarded electronics, landfills and oceans bear the burden of our consumption. The circular economy, however, presents an alternative by keeping products and materials in circulation. Through repair, repurposing, and recycling, waste generation is significantly curtailed, offering a cleaner, healthier world for future generations.
3. Economic Growth and Innovation
Contrary to the notion that environmental consciousness stifles economic progress, the circular economy sparks innovation and economic growth. As companies pivot towards sustainable practices, new business models emerge. From remanufacturing to waste management services, these ventures not only create jobs but also foster a spirit of innovation in the pursuit of sustainability.
Circular Economy in Action
1. Textile Recycling and Upcycling: Redefining Fashion
The fashion industry, notorious for its contribution to pollution and waste, is undergoing a transformation within the framework of the circular economy. Textile recycling and upcycling initiatives are turning discarded garments into new, fashionable pieces. This approach not only reduces the environmental impact of clothing but also challenges the throwaway culture that has dominated the industry.
2. Electronic Waste Management: A Safer Disposal Route
Electronic waste, laden with hazardous components, poses a significant threat to our environment and health. Circular economy practices encourage responsible e-waste disposal, wherein valuable materials are salvaged and harmful substances are safely managed. This safeguards both our planet and our communities from the perils of toxic waste.
Overcoming Challenges and Future Outlook
The transition to a circular economy is not without obstacles. Changing consumer behavior, developing robust recycling infrastructure, and aligning policies require concerted efforts from governments, industries, and individuals. However, the urgency of addressing climate change and resource depletion provides the impetus needed to overcome these challenges. As society becomes more attuned to the benefits of circular practices, the movement gains momentum.
Conclusion: Paving the Way to a Regenerative Future
In a world defined by finite resources and mounting environmental concerns, the circular economy offers a tangible solution. By reimagining the way we produce, consume, and manage waste, we can chart a course toward a more sustainable future. By embracing the principles of durability, sharing, and circularity, we have the power to leave a positive impact on the planet for generations to come.
FAQs
Q1: How does a circular economy differ from a linear economy?
A circular economy prioritizes resource reuse and recycling, aiming to minimize waste and environmental impact, whereas a linear economy follows a linear “take, make, dispose” pattern that leads to excessive resource depletion and waste.
Q2: What role do consumers play in the circular economy?
Consumers play a pivotal role by supporting sustainable products, participating in sharing initiatives, and demanding responsible production practices, thereby driving the adoption of circular principles.
Q3: Can a circular economy be applied to all industries?
Absolutely, the principles of a circular economy are versatile and adaptable to diverse industries, from manufacturing to agriculture, each requiring tailored strategies to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency.
Q4: How can a circular economy promote innovation?
Circular economy practices encourage businesses to rethink traditional models and develop innovative solutions for waste reduction, product design, and resource management, fostering economic growth through sustainable practices.
Q5: How can governments facilitate the transition to a circular economy?
Governments can facilitate the shift by implementing policies that incentivize circular practices, supporting research and development, investing in recycling infrastructure, and fostering collaborations between industries and communities.