Effective writing of funding proposals is always been a meticulous and intricate act, an intellectual challenge!
More you cook your words within the script, more it gets potency. Actually, effectiveness is either the denomination of doing right things or discarding the surplus.
The impression of your proposal, analysis based on facts, planning & management of resources and commitment to the quality workout ensure the life of the relationship between writer and donor.
While writing a proposal, here is the sketch for writer’s orientation:
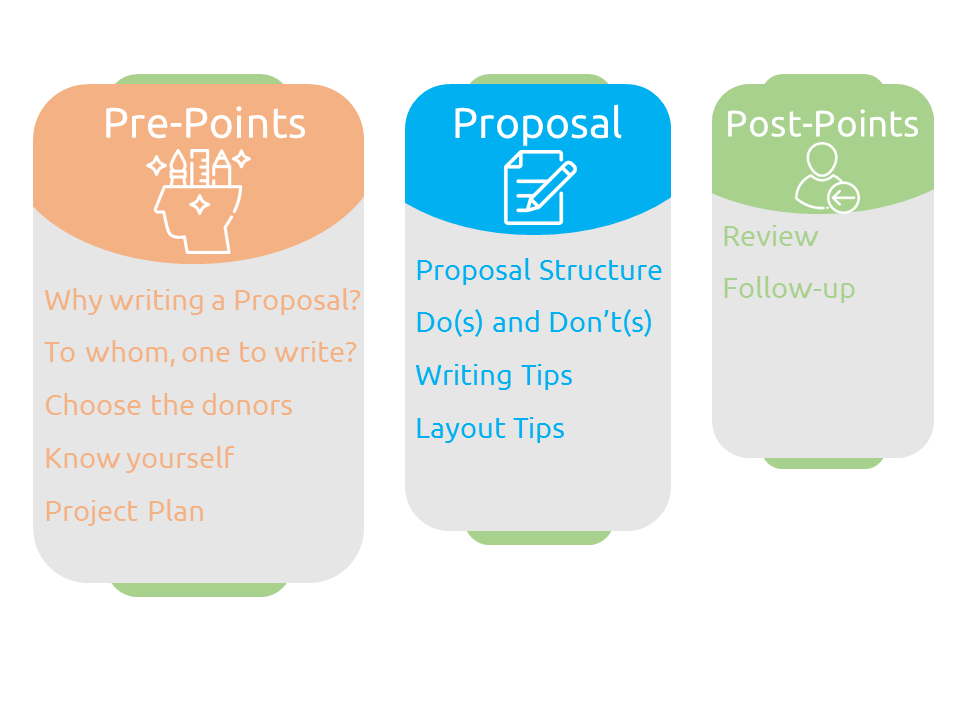
Note: Without the appropriate idea, necessary research and suitable plan, one can’t start writing the funding proposal.
The detail of each of the above-mentioned points is described as below:
Why writing a proposal?
Visualize a clear image of the reasons you are going to write for. Ask yourself a few questions: whether you really need the funds or not; will you justify the funds; how much amount you actually need; how you’ll convince the donor (foundation/company/person) to provide you with the necessary amount and the basis for your relationship with the donor. After self-assessment, you’re well oriented about what you’re going to do, writing of financial proposal in an effective way.
To whom, one is to write?
For enhancing the capital for business or project, one is to require a lot of funds. There are several sorts of agencies, you can write to. The following table will make you clear about the funding agencies:
| Type of Agency | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Government |
|
|
| Small Corporation |
|
|
| Large Corporation |
|
|
| Small Foundation |
|
|
| Large Foundation |
|
|
Choose the donors
You’re writing the proposal for technical experts or decision makers. So, the proposal must be persuasive and technically well compiled. You’ve already gone through the donors but the selection of the most suitable donor matters a lot.
While choosing the donor, following points are quite useful:
- Name of donor, address, telephone, fax number and email address.
- Goals, missions and concerns of the donor.
- Amount of grant, the donor may provide you.
- Limitations and Guidance announced by the donor.
- Deadlines provided by the donors for the consideration.
Similarly, each and every donor expects the following things from you:
- Authentic information, knowledge and understanding regarding you.
- Credible evidence about the success of your project in which you’re going to invest the money.
- Sort of problems in the specified region you may face in promoting the donor.
Know yourself
This simply means your clear image about the project to the donor, self-assessment! By admitting the fact – things are not going to happen in a sole night, you’ve to order your activities in a systematic order. This also assists in building the organizational capacity. The act of knowing yourself can be accomplished by following steps:
Writer’s identity
Above all, it’s important to know that writer’s identity means the identity of the organization because one organization is writing for seeking funds. It includes:
- The overall goal and mission of the organization.
- Logo of the organization must display a visible and meaningful identity.
- The complete biography i.e. competency, experience and community links of your staff members whether professional or non-professional. It also indicates the human resources of an organization.
- Backbones of your organization going to work on the project.
SWOT analysis
This analysis works as a tool which analyses the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats which may further affect the business or project. According to SWOT analysis:
- Strengths: Committed and experienced staff, professional working space and outcomes of your organization.
- Weaknesses: Conflicts and deficiency in technological skills.
- Opportunities: What kind of works the organization can perform effectively.
- Threats: Variation in the focus of donor.
Track record
Track record shows your reliability towards donor. It is just like an evidence of your previous workout. It includes:
- Previous outcomes and impacts.
- Professional and technical competence in working fields.
- Previous successful strategies and good financial management skills.
- Reliable management competence with regard to people and project.
Project plan
One phrase is enough to answer this i.e. “What can we get money for?” This is all about strategic planning and action planning the organization is going to opt for the project. It must reflect context, objectives and process. Likewise:
Context
Depending upon the project, common points you need to know about the context are mentioned below:
- Domicile i.e. country, region and details of the area.
- The economic state of the country.
- National conflicts and issues of the region.
- Health and educational status.
Objectives
By objectives, we mean the outcomes and beneficiaries at the completion of project or business. Objectives are mainly classified into two main categories; one is generic and other is specified. Generic objectives are often related to the overall efficiency of the organization while specified objectives are related to peculiar project or business. These explicitly can be summarized as below:
- The overall objective of the organization must provide an accumulative goal.
- The specified objective must provide an immediate goal to the business.
- It helps in clarifying your agenda and strategy for the development of the goal.
- It also measures the possibility of success in the project or business.
- It develops the framework to compile the project process.
Process
It is the step-by-step planning towards the destination. A process must contain the following core point for the successful achievement of the target:
- Clearly define your actions.
- Decide the venue for the project or business.
- Announce the timeframe i.e. starting and ending dates.
- Calculate the human resources.
- Identify the inputs.
- Mention the outputs.
- Setup a plan for monitoring of the project development.
- Evaluate the whole mentioned process.
- Introduce the timely improvement (if necessary).
Proposal Structure
It’s the most important part of the financial proposal written for business and project. While writing the contents of proposal’s structure, you must keep in mind the word – CROP. It is comprised of the Context, Relevance, Objectives and Process. This helps in visualizing the whole minor and major components of business or project. The main structure consists of the followings:
- Title page
- Summary page
- Page of contents
- Main body of the proposal
- Discussion and conclusion
- Appendices
- Bibliography/References
The following table will clearly explain the above-mentioned bullet:
| Bullet Title | Content | Explanation |
| Title Page |
|
The title must reflect the essence of the whole business or project in the minimum possible words.
It must not be so long. |
| Summary Page | It must display the summary of the proposal.
It varies from proposal to proposal. Generally, It must be 1/3 of the whole discussion regarding project or business. |
To cast the clear image of your proposal within the summary, following points are of vital worth:
The fixed and variable costs |
| Page of Content Outline | Enlist all the main components of your proposal and do numbering as per their pages | It aids the writer to find out the content of interest without the wastage of time.
It costs positive impression on the reader as well. |
| Main body of the Proposal | Here is the use of word CROP – Context, Relevance, Objectives and Process.
The process is planning to do this all. It must be of 4 to 5 pages. |
Keep in consideration the followings:
Moreover, you can also direct the reader towards the appendices for the further details. Discuss both the degree of flexibility and sustainability of project or business in case of addressing some problems from both ends. |
| Discussion and Conclusion | It involves the discussion and conclusion regarding the question – why do you need money?
Must address the financial details and required the budget. |
Conclude in an effective way to make a good impression.
The specific details of the budget must be mentioned in appendices. |
| Appendices | It is comprised of the detail technical descriptions like the timetable, annual reports, financial statement and detail of budget etc. | This is the place where you provide the additional, essential and comprehensive details without making the proposal so long. |
| Bibliography/References | In this section, mention all the references related to business or project. All the references should be in proper order as per their usage in the text. | Enlist all the credible and reliable references for the donors to restore trust. |
Order of sections
Its pivotal purpose is to make you well-guided about the order of sections of the proposal. In other words, it will aid you in making funding proposal structurally correct and credible.
- Donor’s confidential (Name of donor, address, phone, email & fax)
- Business title/Project title
- Summary of funding proposal
- Table of contents
- Background
- Objectives (Both general and specified)
- Process (Resources, inputs & outputs)
- Conclusion
- Budget Summary
- Appendices
- Bibliography/References
- Writer’s confidential (Name, address, phone, email & fax)
Do(s) and Don’t(s)
It is actually the set of points based on the personal experience of expert proposal writers. If you’ll follow them, it will help you make your proposal well compiled. Have a look at them:
| Do(s) | Don’t(s) |
|
|
Writing
Useful tips can be classified into two main categories: Writing tips and Layout tips. We’ll make you able to go through both of these.
Writing tips
- Try to write for a non-technical reader.
- Use simple English.
- Avoid making lengthy sentences.
- Construct the sentence in an active way than a passive way.
- Your proposal must be grammatically true.
- There should be no spelling mistake.
- Revise and rewrite as per situation (if necessary).
- Avoid exaggeration and overlapping.
- Repetition must be avoided.
Layout tips
- Always use the understandable font like Arial.
- Present your text in headings and subheadings.
- Highlight or bold the important notes.
- Place the nominal gap at edges, among the lines and between the words.
- Text colour should be black.
- Don’t mess the text.
- Do numbering of the pages.
- Bind the document in the correct order.
Follow up
Till yet, you’ve structured the financial proposal for your business or project. Is it the end? Definitely, No! It’s the beginning. After submitting the proposal, two types of follow up can be observed at the professional level: Follow up the proposal and follow up grant. It forms the strong basis for the good customer-client relationship. While going for the follow-up, the writer must be pleasant, polite and persuasive enough to make the reader comfortable to read.
Follow-up Proposal
After the successful submission of the proposal, if you are not being replied within the expected time, you always follow up your proposal to know the status. To follow up a proposal, one may simply write an Email or Letter. Following are the most common reasons for following up:
- To check whether the proposal is meeting the selection criteria or not.
- To know whether it is accepted or rejected.
- When will final notice be issued about the proposal?
- To discover the causes of acceptance or rejection.
Follow-up Grant
After the successful approval of your funding proposal, you may write to follow up the grant which is going to be issued to you as per request. It also displays the open doors of the donor for you. Now, you can follow up as:
- To pay regards and thanks for fruitful response by the donor.
- To keep the bilateral communication open at all times.
- To update the donor about the usage of funds.
- To report the donor about the recent progress.
- To ensure them that funds are being utilized as mentioned in the proposal.
- To invite the donor to your event as your honourable guest. It really works!
- To make them feel reliable.