This tool is used to translate nucleic acid sequences into the amino sequence of the protein. You may read more about 6 Frame Translation below
Standard symbols for polymorph nucleotides:
| Y | C,T | V | A,C,g |
| M | A,C | N | A,g,C,T |
| K | g,T | ||
| S | g,C | H | A,C,T |
| W | A,T | B | C,g,T |
| R | A,g | D | A,g,T |
DNA Reading Frames and 6 Frame Translation
If the genetic code is read in nonoverlapping triplets, there are three possible ways of translating any nucleotide sequence into the protein, depending on the starting point. These are called reading frames. Three reading frames of each of the two DNA strands makes 6 reading frames in a double stranded DNA.
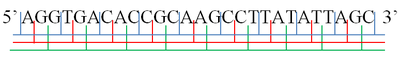
Each gene represents a particular protein chain, and each protein consists of a particular series of amino acids. The relationship between a sequence of DNA and the sequence of the corresponding protein is called the genetic code. In any given region of DNA, only one of the two strands codes for a protein, so we write the genetic code as a sequence of bases (rather than base pairs). The genetic code is read in groups of three nucleotides, each group representing one amino acid. Each trinucleotide sequence is called a codon.
A gene includes a series of codons that are read sequentially from a starting point at one end to a termination point at the other end.Written in the conventional direction, the nucleotide sequence of the DNA strand that codes for protein correspond to the amino acid sequence of the protein.
Nonoverlapping implies that each codon consists of three nucleotides and that successive codons are represented by successive trinucleotides.