Genetic engineering is the modification of genes that code proteins vital to the functioning of a living being.
“It is the process of manipulating the organism’s genome by the modification of the genes.” Recent advancements also found the role of non-gene DNA regions also. So, Genetic engineering can involve the manipulation of those regions also.
It uses techniques from biotechnology and bioengineering to modify an organism’s genetic makeup. Genetic engineering then results in modification of an organism’s genetic makeup. Alternate words for genetic engineering are recombinant DNA technology, genetic modification, genetic transformation and genetic alteration. The objective of genetic engineering is to insert few new traits to the individuals that are not already found in the organism by taking the DNA that code for specific genes (traits) and then inserting it to the desired organism.
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the major player in genetic engineering as it codes for the gene that plays role in functioning, development, reproduction and many controlling many traits of the individual. It has four bases Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and thymine. Genetic engineering is not only limited to anyone specie but it is being done in animals, humans, plants, microorganism.
How is genetic engineering done?
For genetic engineering to be done it is important to identify the gene of interest with the desired trait or function. Genetic engineering in organisms includes the use of vectors, plasmids, microinjection, biolistics and chemicals.
Plasmids
The plasmid is the circular DNA found in bacteria. Gene of interest is isolated and cut with restriction enzymes. With the same restriction enzyme plasmid is cut. Gene of interest is incorporated into the plasmid with the help of enzyme ligase. Then this plasmid is inserted back into the bacterial cell and gene of interest replicates with the plasmid in the bacterial cell.
Vectors
Vectors are usually viruses and as it is known that virus causes an infection. In to these vectors gene of interest is incorporated by cutting the vector and the foreign DNA with the same restriction enzyme. When the virus replicates and causes infection, in this way gene of interest is incorporated into the host cell/desired organism. Vectors have the origin of replication, selectable marker, and target site for the insertion of the gene of interest.
Microinjection
In microinjection, the target is to incorporate the new gene into the recipient or host cell. This process doesn’t require the use of plasmids or vectors. In this technique, fine-tipped glass needle is used for the injection of the new gene into the recipient cell.
Biolistics
Biolistics method also known as the gene gun method, it uses metals particles that are coated with the gene of interest that we want to transfer. Then gene gun transfer the metals coated with the gene of interest into the recipient cell.
Use of chemicals
Chemicals are also being used for direct transformation of the gene of interest into the host cell. Calcium phosphate, Cationic Lipid, and other polymers like poly-L-lysine, polyphosphoester, and dendrimers.
Practical Examples of Genetic Engineering
Genetic Engineering in Humans and Animals
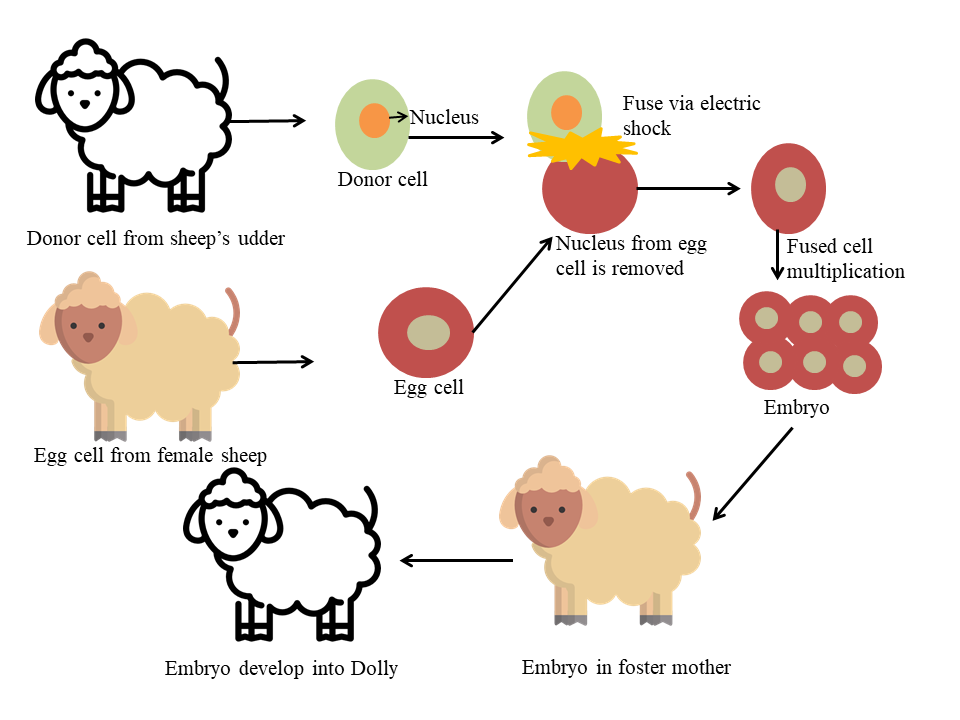
Most commonly known example is cloning, Dolly sheep that was the genetically identical copy of an organism. Genetic engineering can be used in gene therapy, to cure diseases like cancer, sickle cell anaemia. It is also used in treating, diagnosing the genetic disorder.
Enhanced milk production in the animals is also done by the use of genetic engineering. This also helps to produce infant with desired traits such as intelligence, and other phenotypic traits known as designer babies. Biosensors that can monitor the drug delivery to the target or any change in the nucleotide sequence.
Genetic Engineering in Plants
Roundup Ready crops, the genetically modified herbicide-resistant crops. Transgenic/ genetically modified crops with drought, heat, salt, and insecticide resistant properties. Genetic engineering also helps to produce golden rice with rich components of beta-carotene (vitamin A).
Genetic Engineering in Microorganisms
Genetic engineering helps in the production of some recombinant vaccines, production of insulin. Genetic engineering also produces recombinant pharmaceutical. Genetic engineering can help in the development of organisms that have the ability to sense the environmental pollutants.
Ethical issue and Genetic Engineering
This presents the maximum number of possibilities from increasing the crop production to preventing and treating diseases. It is like Playing with God or Playing with nature. Making clones of the existing one give rise to such kind of issues. The gene inserted for gene therapy may have the harmful effect to the human health. Cross-species boundaries are also one of the main issues.
It is to insert the gene of interest from specie to another species. Invasiveness of procedure because a large number of animals are being sacrificed in the experimental setup. Once genetic engineering is done it cannot be reverted back. It is going to have the harmful effect to the environment as well.
Featured Image: BloodyBee/Flickr